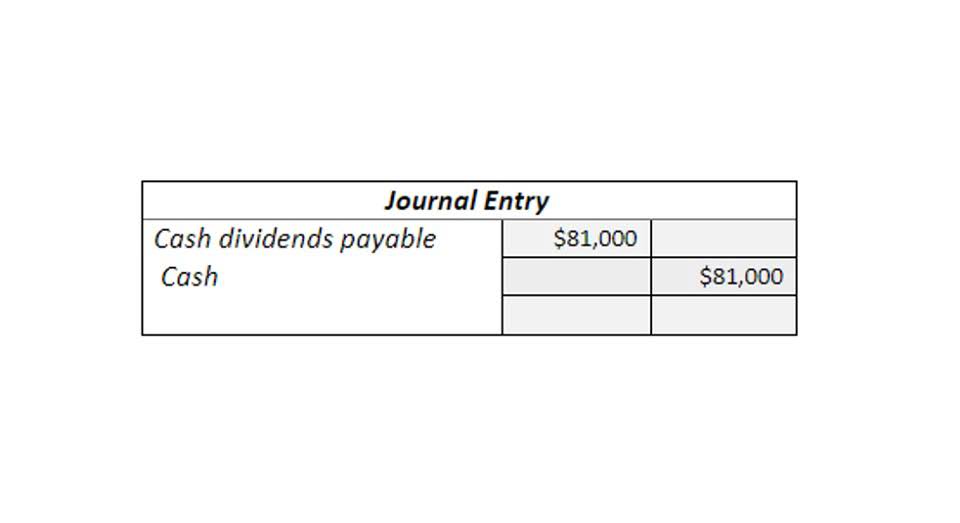
Journal entry for amortization of prepaid insurance

The total assets remain unchanged, as the increase in prepaid insurance is offset by the decrease in cash. Several purchases that you make in small businesses can be considered prepaid expenses. The transaction will reduce the prepaid insurance and increase the insurance expense on the income statement. Insurance premium is the amount of money that an individual or company paid to the insurance company to get the insurance service. The customers pay the insurance premium, so they will get the insurance cover over their health, accident, and even life insurance. Repeat the process each month until the rent is used and the asset account is empty.
Prepaid Expenses Journal Entry Example
This process helps in accurately reflecting the expense in the periods that benefit from the prepaid amount. Reviewing and adjusting prepaid expenses is crucial for maintaining accurate financial statements and ensuring that expenses are matched with the revenues they help generate. The most-common examples of prepaid expenses in accounting How to Invoice as a Freelancer are prepaid rent from leases, prepaid software subscriptions, and prepaid insurance premiums. Below you’ll find a detailed description of each one as well as detailed accounting examples for each.

Accruals in Ledger Accounting
A simultaneous entry is also recorded, which reduces the company’s cash (or payments account) by the same amount. Prepaid expenses are generally considered a current asset on the balance sheet unless they are not incurred for more than 12 months, and this is very rare. Prepaid insurance is recorded as a debit to the asset account and as a credit to the cash account. As the prepaid insurance is consumed, an adjusting journal entry is made as a credit to the asset account and as a debit to the insurance expense account.
Accrual basis vs. cash basis
In accounting, we usually amortize the prepaid insurance that we have paid in advance in order spread the insurance cost over the period that it covers. In this case, we can make the journal entry for the amortization of the prepaid insurance by recording the expired cost of the insurance as an expense on the income statement. To create your first journal entry for prepaid expenses, debit your Prepaid Expense account. This account is an asset account, and assets are increased by debits. Credit the corresponding account you used to make the payment, like a Cash or Checking account.
- Based on this, the first component is the current year’s expense, since it is relevant to the timeline for which the financial statements are being prepared.
- Knowing the basic journal entries in the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles system will make anyone’s life easier, but especially managers.
- At the end of June 202X, the company has consumed the insurance service for a month.
- You’ll need to debit the Prepaid Expense account (an asset account) and credit the account you used to pay, like Cash or Checking (Patriot Software).
- This concept is crucial for prepaid expenses, which are payments made in advance for goods or services to be received in the future.
Thus, out of the $1,500, $900 worth of supplies have been used and $600 remain unused. The $900 must then be recognized as expense since it has already been used. Take note that the amount has not yet been incurred, thus it is proper to record it as an asset. Company A signs a one-year lease on a prepaid insurance journal entry warehouse for $10,000 a month. The landlord requires that Company A pays the annual amount ($120,000) upfront at the beginning of the year. Plus, there are questions I received from real bookkeepers/business owners who needed to know how to enter their insurance proceeds from property damage to which you can read my answers.
- It is also important not to confuse a prepaid expense with an accrued expense.
- We’ll keep it real, toss in a dash of humor, and by the end, you’ll understand why these adjustments are essential for your financial statements—not just some accounting mumbo jumbo.
- Insurance is a great example of a prepaid expense because it is usually paid in advance.
- Of the total six-month insurance amounting to $6,000 ($1,000 per month), the insurance for 4 months has already expired.
- When a business pays for a service or product before its actual use, it records the payment as a prepaid asset.
- When you buy the insurance, debit the Prepaid Expense account to show an increase in assets.
- Since you have yet to receive the benefit, you consider the amount paid as an asset.
The company recorded the December 1 payment with a debit of ₹7,000 for Prepaid Insurance and a credit of ₹6,000 for Cash. The Prepaid account expenses must be adjusted on December 31 to reflect a balance of ₹5,000, as the amount prepaid decreases by ₹2,000 per month. The journal entry is debiting prepaid insurance $ 120,000 and credit cash $ 120,000. The journal entry is debiting prepaid insurance and credit cash out. The insurance premium will be the expense for customer over the insurance coverage. Both companies must follow bookkeeping the matching principle, they record revenue and expense only when the service is consumed and provided.

By spreading the expense over the periods it benefits, businesses can better manage cash flow and budgeting. Now if this were a short-term lease, then a prepaid asset would be recognized on the balance sheet for prepaid rent expense. However, under the new lease accounting pronouncements, the guidance eliminates recognizing prepaid assets on the balance sheet related to leases exceeding a total lease term of 12 months. Rather, any prepaid rent pertaining to a long-term lease would be rolled into the ROU asset balance recognized on the balance sheet. Under the accrual method, no expense is recorded until it is incurred.
Imagine ABC Company decides to insure its truck and pays $1,200 for a one-year policy on December 1, 2022. In the company’s books, this prepaid insurance is an asset—specifically, a current asset—because it covers a period within one year. Prepaid insurance is commonly recorded, because insurance providers prefer to bill insurance in advance. If a business were to pay late, it would be at risk of having its insurance coverage terminated. CPAs need to know how to correctly classify and adjust prepaid assets. Prepaid Insurance is the insurance premium paid by a company in an accounting period that didn’t expire in the same accounting period.


دیدگاه خود را ثبت کنید